Data Center Cooling
Every piece of IT equipment that consumes power produces heat in return. The wrong data center cooling solution for the environment can result in higher costs and increased risk of downtime.
When designing data center cooling architecture for your data center or IT environment, it is important to keep three things in mind: heat removal method, air distribution type, and the location of the cooling unit.
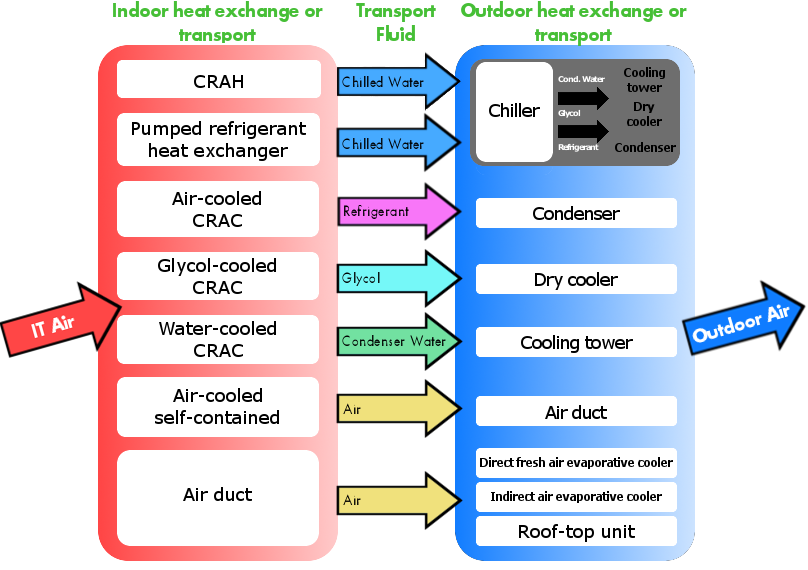
Heat Removal
The removal of hot air could be as simple as an air duct, but generally is done using a heat exchanger to transfer heat energy from one fluid to another (e.g., from air to water). 2NSystems can help you understand fundamental heat removal methods used to cool IT environments, and to select the best one for your data center cooling application.
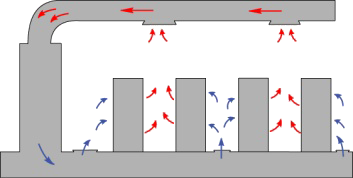
Air Distribution
There are nine basic ways to distribute air in data centers and network rooms that are a combination of the three basic approaches to distribution, used in the supply or return path:
- Flooded: The only constraints to air flow are the walls, ceiling and floor of the room.
- Targeted: A mechanism (e.g., duct, perforated tile, etc.) directs the airflow within 3 meters (10 feet) of the IT equipment intake or exhaust.
- Contained: The IT equipment air flow is completely enclosed.
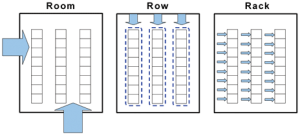
Location
2NSystems can also help you choose the proper approach –room, row, or rack-based–for your application.
- Room: This approach is time consuming to implement and performs poorly at higher densities, but it offers simplicity and cost advantages at lower density.
- Row: A modular, flexible approach, row containment offers the speed and density advantages of rack approach but with costs similar to room approach.
- Rack. This is the most flexible approach and the quickest to implement. It achieves extreme density, but at higher cost.
- The trend is toward row-based cooling for smaller data centers and room-based cooling with containment for larger data centers.
Size
IT environments vary a great deal in size and shape. A large data center is going to have very different needs and requirements than a small network or server room.
Large Data Centers
An effective solution for large data center cooling is the EcoBreeze solution, a modular air economizer that provides the most favorable TCO for large facilities. It offers the highest efficiency by maximizing “free cooling” hours in most climates by using multiple modes of operation.
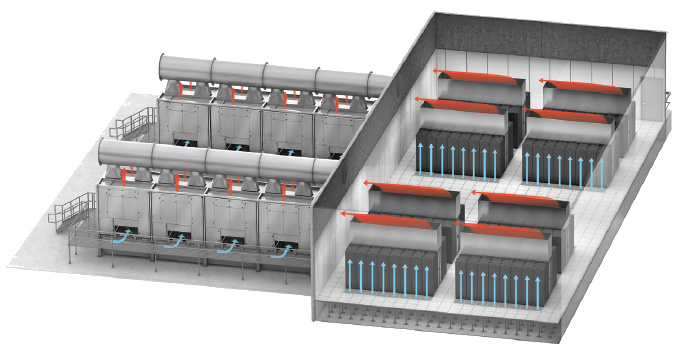
Medium Data Centers
The Unifair solution is popular for medium-sized facilities due to its flexibility, efficiency, and lowest first cost. Utilized within raised floor environments, it offers flexible, intelligent temperature and humidity control to provide precision cooling at the room level.
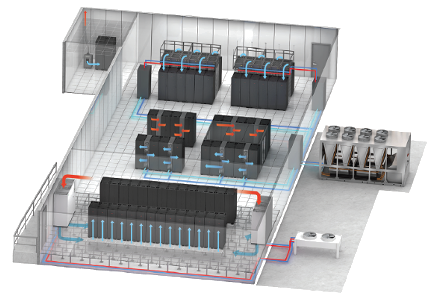
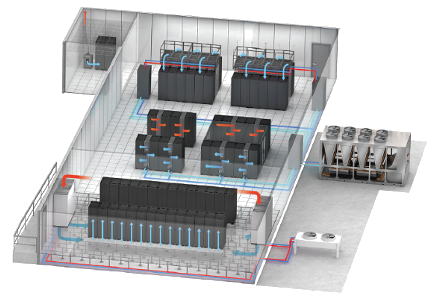
Small Data Centers
InRow cooling products are optimal for smaller data centers, with the predictability of the close-coupled approach and integrated rack and row level temperature control. This also makes them well suited for high-density zones within larger data centers to create a hybrid cooling system.
To maximize data center cooling efficiency and predictability in any IT facility, the EcoAisle containment system minimizes hot or cold air recirculation and improves cooling system performance. The improved airflow enables higher density cooling with any of our cooling solutions, which can further reduce energy consumption and save valuable data center space. Customers can save up to 30 percent in operational costs versus an uncontained system.
Network and Server
Network closets and server rooms are often converted offices or utility closets that were never designed to house IT equipment. They either have no planned cooling or depend upon the building HVAC, which doesn’t provide adequate cooling and can reduce the life of the equipment. Cooling solutions in these confined environments need to have the smallest footprint possible, and should be flexible for easy deployment and redeployment. Uniflair and InRow Direct Expansion products provide a wide range of options to deal with the varying conditions within network and server room environments.
